Ketamine infusion therapy can be effective in treatment resistant depression with a 70% response in patients who have failed multiple other therapies including ECT and TMS. Some patients simultaneously get TMS treatment (transcutaneous magnetic stimulation) with ketamine infusions and find the combination to be even more effective. We combine IV B complex and IV vitamin therapies with the infusions to produce even better results as the vitamins allow the underlying enzymes that produce serotonin (the happiness molecule) and dopamine (the molecule of reward) to have improved efficacy. IV scopolamine prior to the ketamine enhances results as well. Scopolamine has studies demonstrating an antidepressant effect as well as promoting calmness and preventing nausea. No referral for treatment is needed. We don’t alter your medication regimen initially, but generally initiate the ketamine infusions, nasal sprays, and oral ketamine treatments to augment your current medications. For those with medication side-effects, you can use ketamine infusions to wean off your medications. Ketamine infusions generally are done as a series of 6 infusions either twice or three times a week with monthly maintenance infusions as needed. Patients who respond generally start a home-based ketamine nasal spray or oral ketamine regime for aftercare at NOVA Health Ketamine Treatment Center in Fairfax, Virginia. Ketamine is effective in depression treatment, OCD, PTSD, chronic pain, bipolar disorder, and several other conditions. If you are looking for a ketamine treatment provider near me or a ketamine clinic, call us today for an immediate appointment.
NOVA Health Recovery is a Ketamine Treatment Center in Fairfax, Virginia (Northern Virginia Ketamine) that specializes in the treatment of depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, OCD, and chronic pain such as CRPS, cluster headaches, and fibromyalgia using Ketamine therapies, both infusion and home-based ketamine nasal spray and oral tablets. We also offer addiction treatment services with Suboxone, Vivitrol, and Sublocade therapies for opiate addiction as well as alcohol treatment regimens.Contact us at 703-844-0184 or at this link: NOVA Health Recovery Ketamine Infusion Center
Neurobiology of stress and antidepressants- synaptic connections
Depression:
- Economic costs $100 billion a year
- 17% of the population suffers from depression
- Women affected twice as often as men
- Most treatments require weeks to months to work
- Neuronal atrophy and loss of neurotrophic factor support play a major role in depression
There is loss of brain tissue in depressed patients:
- Decreased prefrontal cortex (PFC) volume (involved with decision making and executive functioning) and hypofunction is noted with correlation to disease severity clinically in bipolar patients and depressed patients
- Decreased size in the hippocampus (the area of memory) The volume of the hippocampus is reduced more and more with longer duration of depression. This can be reversed with antidepressant treatment.
There is both structural loss and changes in Major depressive disorder (MDD) as well as neurochemical changes. These are reversible with treatment.
What contributes to the loss of volume in MDD?
- Chronic stress leads to depression and decreases synaptic connections in the PFC and hippocampus Stress Induces a Decrease in Dendritic Spine Density and an Increase in Segmentation at Apical Tuft Dendritic Tips.
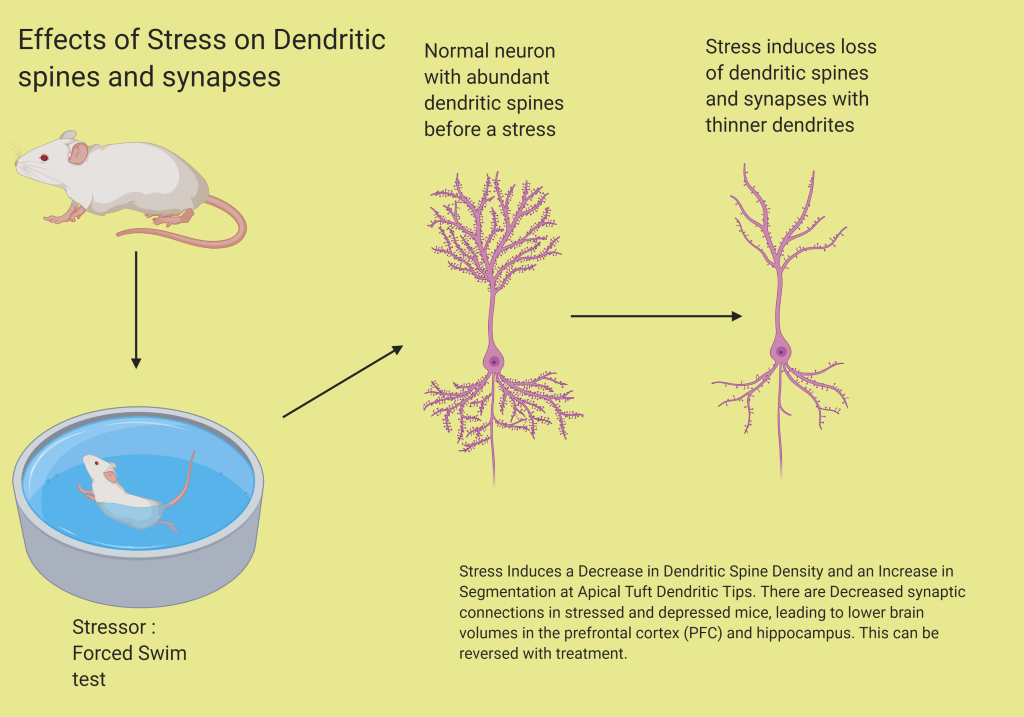
- Stress can influence the PFC and hippocampus in terms of synapse connections, apical dendrites, and neurogenesis. There is a retraction of synapses rapidly with stress and depression. Decreased synapses is seen in the PFC of patients who committed suicide.
- Loss of connections decreases control of mood, cognition, and emotional dysregulation. The result is depression.
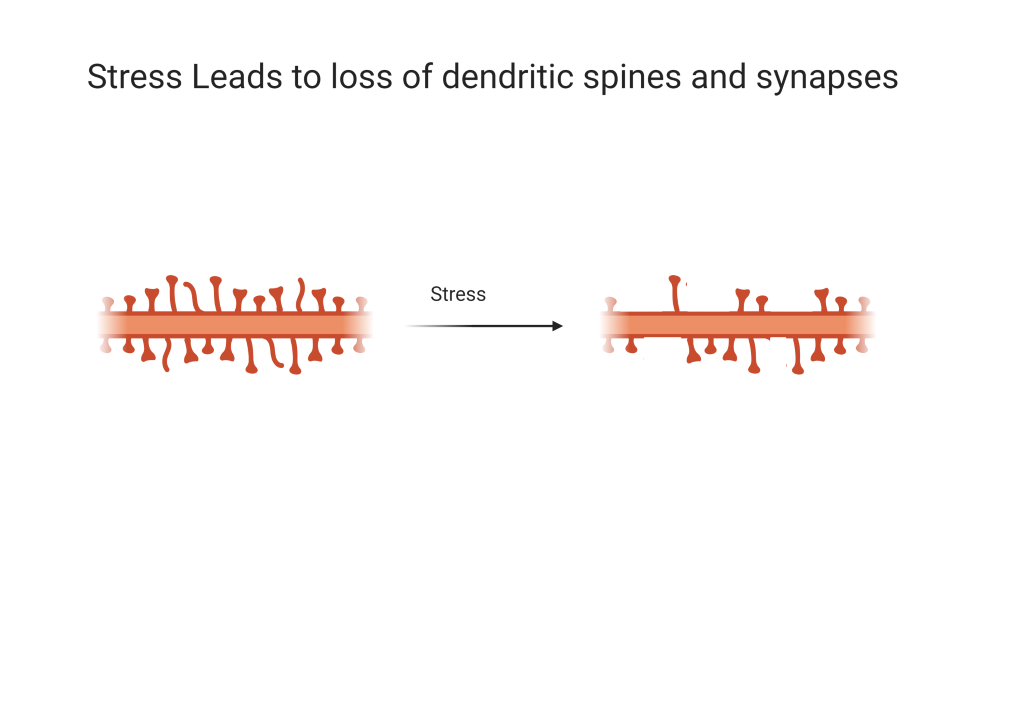
The atrophy of neurons and loss of synapses leads to emotional dysregulation.
What is the impact of antidepressants?
Most antidepressants block monoamine reuptake such as serotonin and norepinephrine, but they don’t directly impact spine number and function. They can block the effects of stress, but this can take months for them to work. They are only effective in 1/3 of patients on the first trial. It may take years to get the treatment right. 1/3 of patients are treatment resistant (MDD).
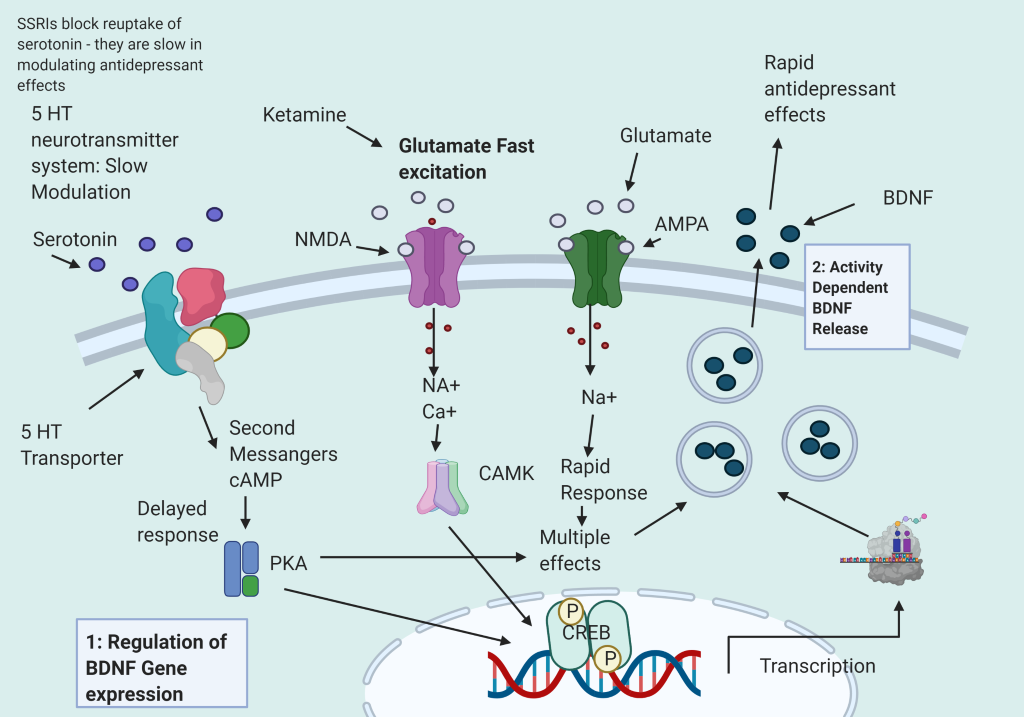
SSRIs influence second messenger systems too SLOWLY modulate the responses of neurons with neuroplasticity and neurogenesis.
Drugs acting through glutamatergic neurotransmitter systems directly act on the AMPA and NMDA receptors to rapidly gain effect as an antidepressant. An example is Ketamine.
Ketamine is a rapid-acting antidepressant. In a study by Berman in 2000, a single dose of ketamine resulted in an antidepressant effect within 72 hours of administration. Link to the graph.
Ketamine blocks the NMDA receptor at the GABA interneuron and allows for a glutamate brief burst to produce Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) that increases neuroplasticity.
Several other studies replicated this including Carlos Zarate in 2006 demonstrated reduction of depression in 2 hours to a single ketamine dose given IV. This is rapid and lasted 7 days after a single dose, but many relapse back after that point.
In Bipolar depression, Zarate (2012) demonstrated rapid improvement in depression in 40 minutes lasting 7 days at least.
Suicidal ideation is decreased rapidly as well as demonstrated by Price et al (2009) and Larkin (2011) which showed that there was a rapid reversal of suicidal ideation even 10 days after a single IV ketamine dose.
- 36,000 individuals die a year from suicide and 23% of these patients were on antidepressants at the time of the suicide.
Multiple replication studies have demonstrated the same improvement in depression with ketamine infusions.
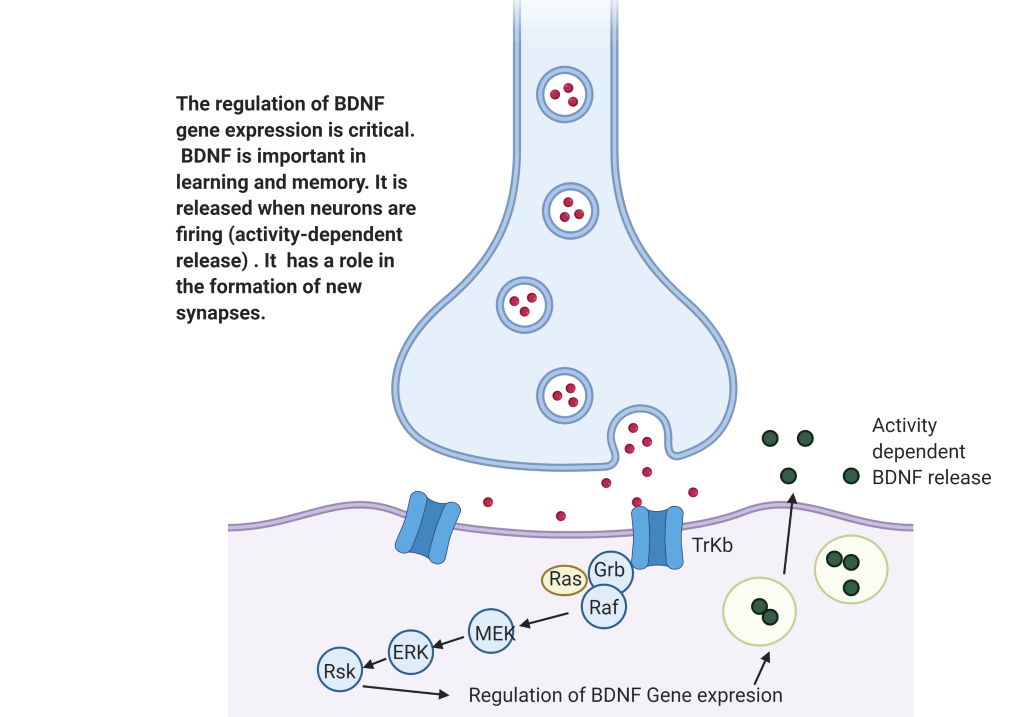
Image from: Aan Het Rot M, Zarate CA Jr, Charney DS, Mathew SJ. Ketamine for depression: where do we go from here?. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72(7):537-547. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.05.003
Ketamine causes:
- Rapid remodeling of synapses in response to glutamate activity
- Typical antidepressants do NOT affect the synapses directly
- Ketamine affects the number and function of synaptic spines.
Stressed and depressed patients have dendritic spines that are fewer in number than in non-depressed individuals.
Glutamate is involved in learning and memory. Ketamine, through regulation of glutamate, causes increase synapse formation.
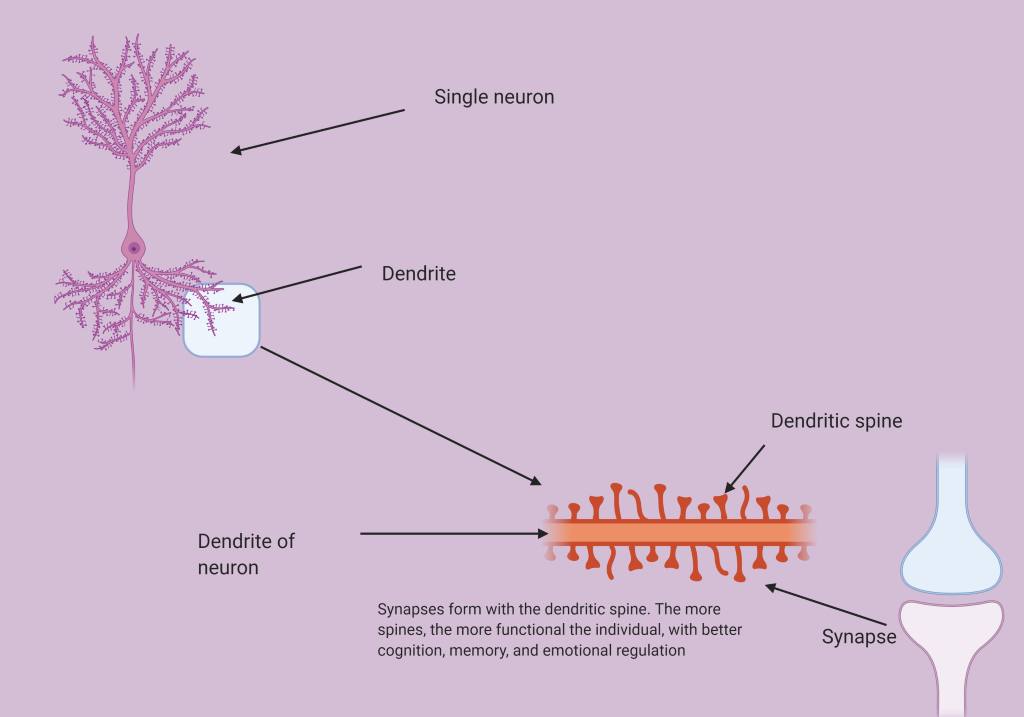
Ketamine rapidly increases neuronal connections.
The size of the spine and the bigger the connection creates greater function at the synapse. In a study by Li et al (Science 2010) it was shown that ketamine rapidly increases synaptic protein formation in the prefrontal cortex (PFC – the C.E.O of the brain) by increasing spine number and the number of mushroom or high-quality spines. Proteins involved in the synapse production included GluR1, PSD95, and Syn1.
Ketamine:
- Increases the size of the spines (mushroom spines)
- Increases spine density
Proteins required to form these spines include: (These proteins are required to build synapses and spines)
- GluR1
- PSD95 (post synaptic density protein 95)
- Syn1 (Synapsin)
These proteins can be measured after a single dose of ketamine and were found to be increased. This occurs within 2 hours of the ketamine administration. This lines up with clinical effects as seen in Zarate et al (2006) in which the antidepressant effect of ketamine is noted at 2 hours.
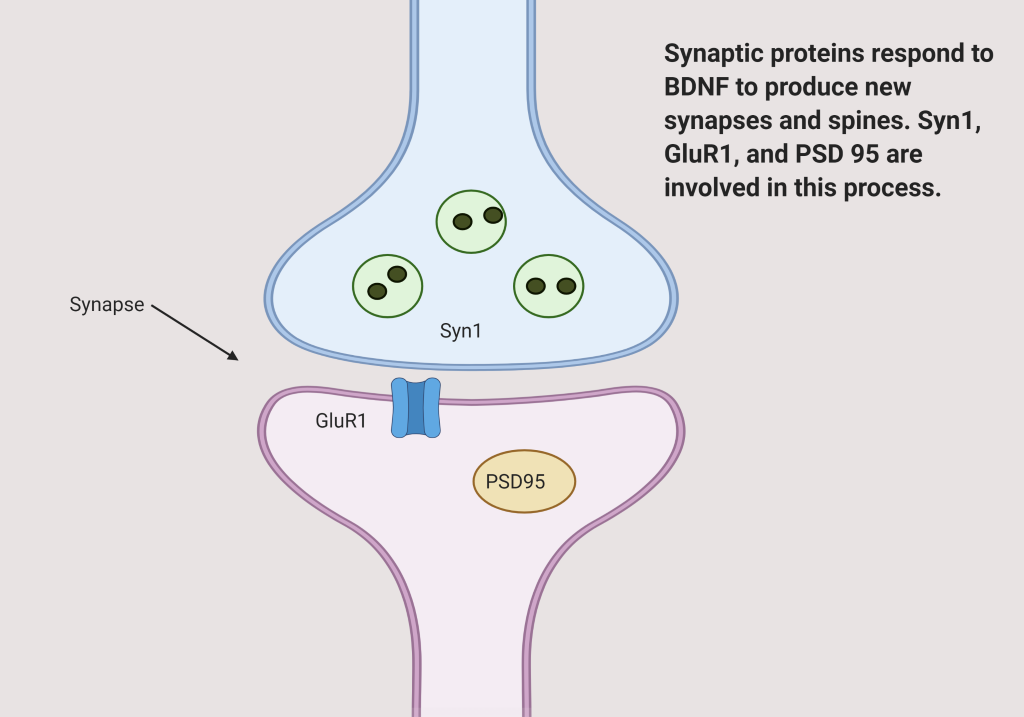
The increase in the synaptic connections occurs at the same time as the therapeutic responses. This response is present even at day 7, but drops off at day 14, as does the therapeutic response.
Ketamine has rapid actions in rodent models. Models that measure helplessness and despair include the forced swim test and learned helplessness model of depression. Stress leads to anhedonia and depression in rodents. This is shown by decreased intake of sucrose by rodents after stress or giving up in a swim test when forced to swim in a beaker. So chronic unpredictable stress causes depressive symptoms in mice and decreases synapses on histological sectioning.
Ketamine reverses the depressive symptoms and increases the synapse numbers.
Ketamine rapidly reverses spine and behavioral deficits caused by chronic stress (3 weeks or more). The pathophysiology and treatment of depression is associated with the number and function of synaptic connections. Ketamine reverses depression and anhedonia.
What is the mechanism by which ketamine increases spine number and function?
Ketamine influences GABA inhibitory neurons that actively control glutamate release. Ketamine turns off the GABA interneurons to allow the Glutamate release from presynaptic neurons and thus produces the antidepressant effect.
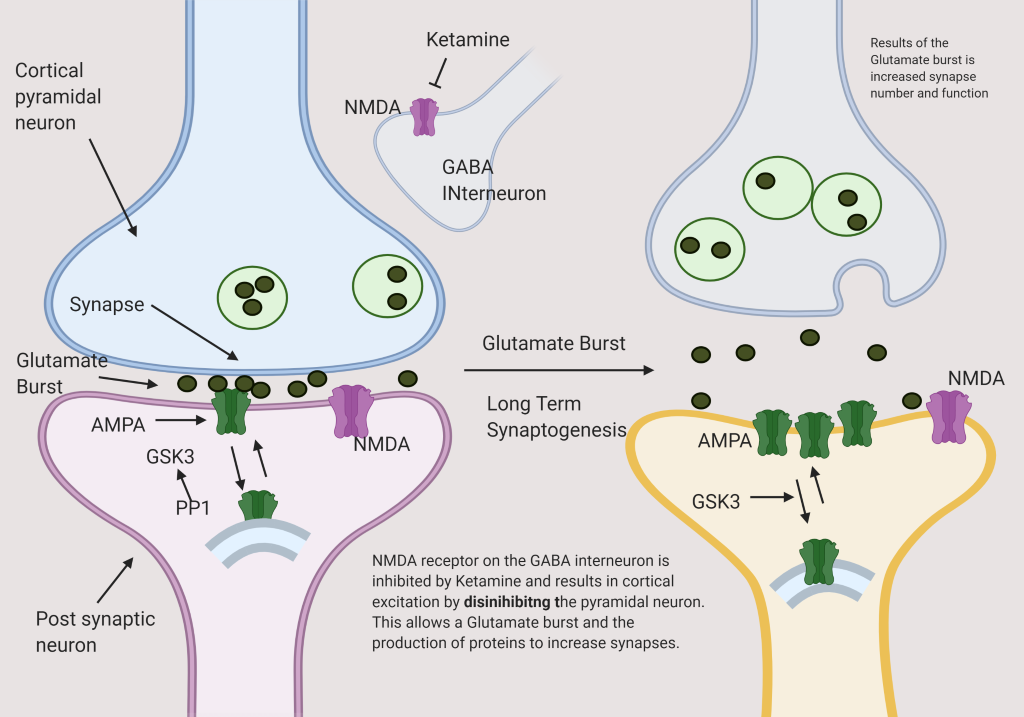
MTOR (mammalian target of Rapamycin) mediates the protein synthesis dependent learning and initiates the translation of proteins in the brain to increase synaptic spines. MTOR is present in dendrites.
Ketamine upregulates mTOR and causes the production of synaptic proteins, spine number, and eventually antidepressant behavior. The synaptic proteins include GluA1 and PSD95.
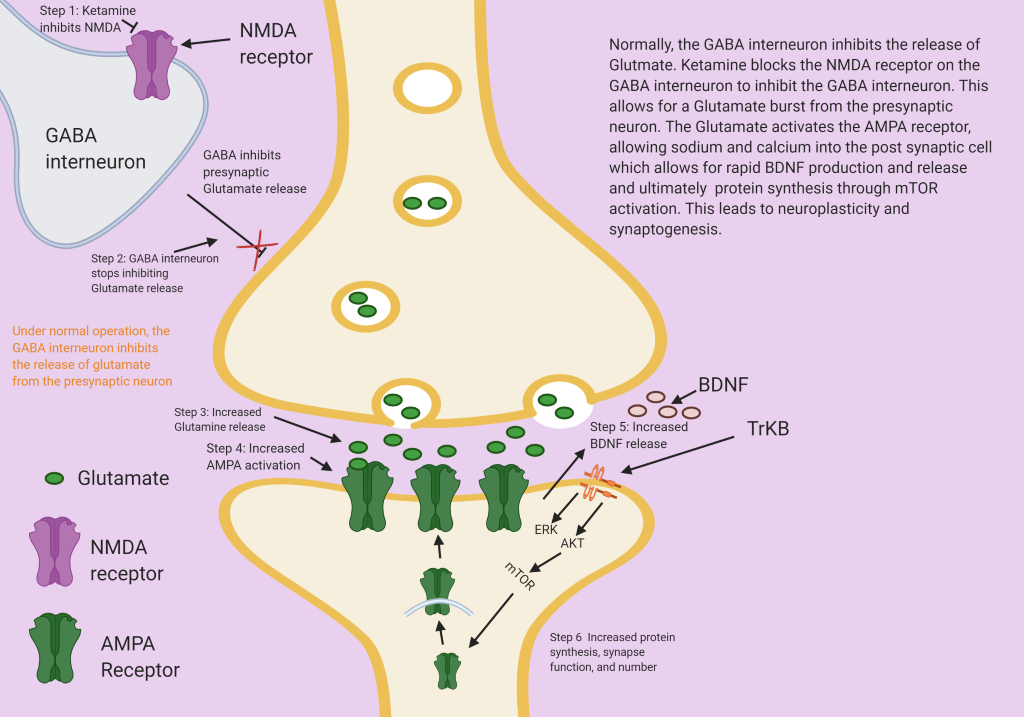
A major neurotrophic factor in the brain is Brain Derived Neurotrophic factor (BDNF). It guides neurons and allows them to survive. In the adult brain BDNF regulates neuronal function, neuronal growth and survival. This is important in learning and memory.

- BDNF is decreased in depression
- Other neurotrophic factors are decreased in depression such as VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and fibroblast growth factor. These all increase with antidepressant treatment.
The BDNF Val66/met polymorphism is a SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) that can decrease the production of BDNF and is present in 25% of the population. The BDNF Met SNP results in decreased BDNF and is associated with reduced episodic memory, reduced memory performance, and decreased executive functioning. There is also decreased hippocampal volume in normal subjects with this allele as well as in MDD and Bipolar patients.
There is an increased vulnerability for depression in people with stress and the BDNF Met allele, especially with early life exposure. The Met allele decreases the release of BDNF from the terminals, however the total production of BDNF is normal. Ketamine induction of dendritic spines and its antidepressant behavior is blocked in BDNF Met mice.
The Met/Met allele blocks the release of BDNF. The Met carriers had a 50% reduction response compared to Val carriers in one study. So, the Val66Met allele can be used as a marker to identify people who may respond to ketamine or not.
The ketamine response requires BDNF release to produce its antidepressant response. Control of mood and emotion require synaptic integrity of PFC neurons. Ketamine produces nascent spines in the PFC and restores spines lost due to stress and depression.
Relapse is associated with the loss of synaptic connections. There may be ways to keep the effect of the response stabilized with add-on therapy.
The control of mood and emotions requires synaptic integrity with the PFC and inhibitory connections with the amygdala and other brain regions. Regions like the amygdala are involved in fear and anxiety. The PFC also interacts with the dorsal raphe and nucleus accumbens (a mesolimbic region of reward) to regulate mood as well as the hippocampus (involved with memory)
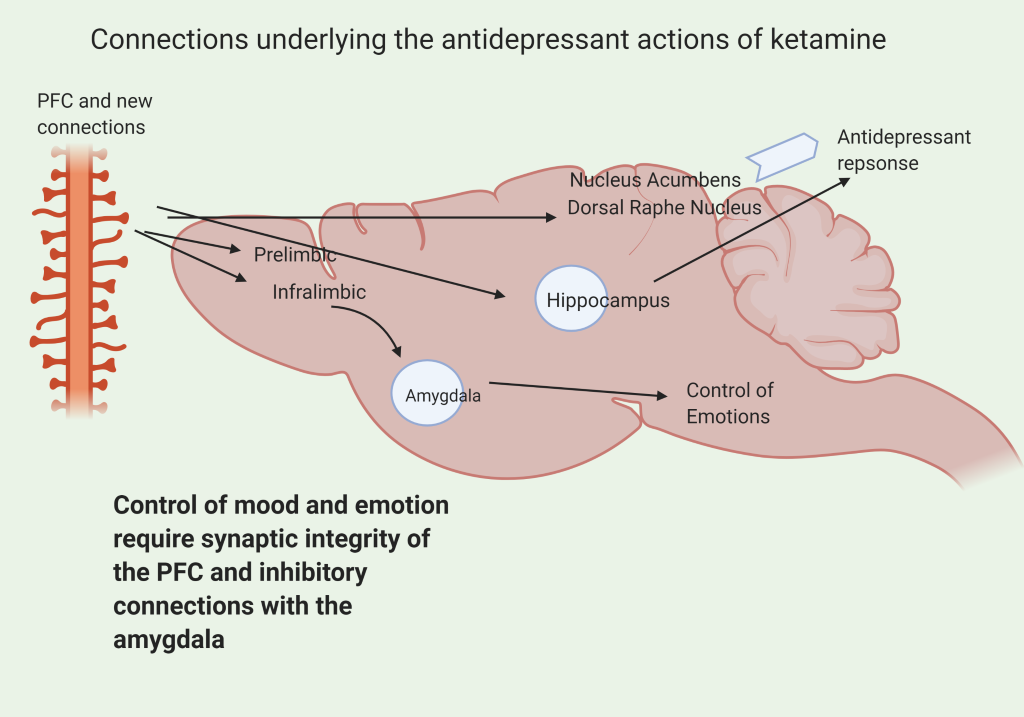
Side effects of ketamine:
- Produces psychomimetic effects acutely
- Nausea
These effects are transient within the first hour. The antidepressant effect can last a week from a single infusion.
What mediates neuronal atrophy in stress? Relatively mild stress can cause neuronal atrophy within a week. The consequences include MDD. PTSD, cognitive deficits, and other mood disorders.
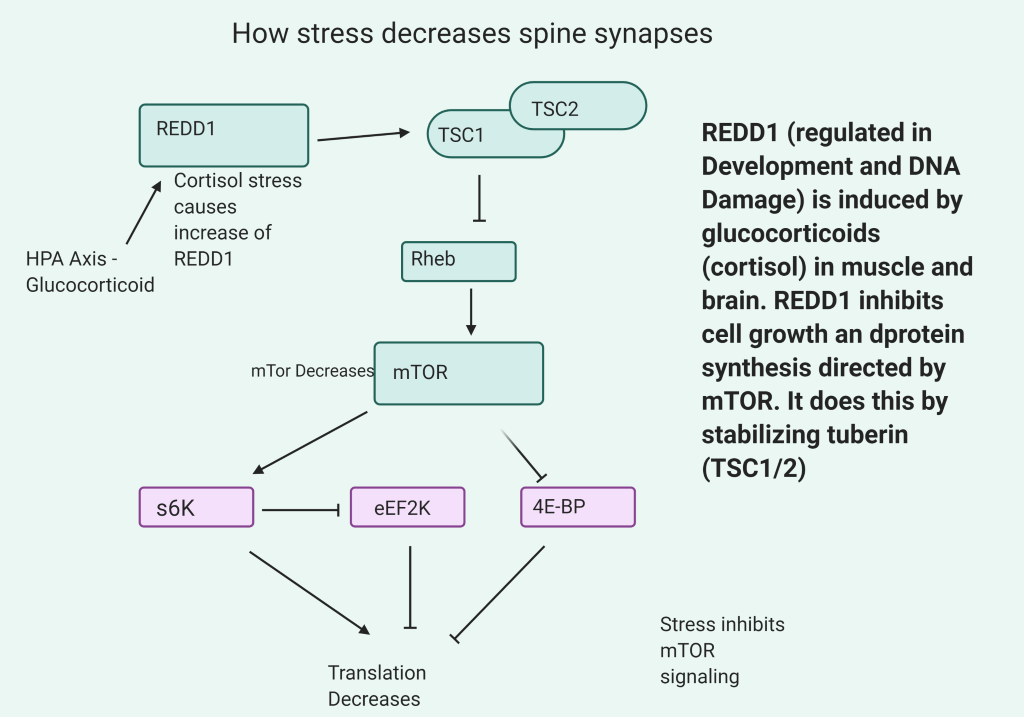
- Increase of REDD1 causes the decrease in mTOR functioning and this decreases synapse formation
- Stress and increased cortisol form HPA stress increases REDD1 to cause the decrease in mTOR.
- REDD1 is increased in postmortem dorsolateral PFC areas of the brains of MDD patients (65% increase)
- This is involved in the synaptic dysregulation seen in MDD.
- Mice with a knockout of REDD1 are resilient to synaptic and behavioral deficits after chronic stress.

Summary:
- Stress decreases BDNF and mTOR signaling resulting in decreased synaptogenesis and spine formation
- Increases in REDD1 will decrease the activity of mTOR thus decreasing BDNF production. Stress and activation of the HPA axis produce the increase of REDD1.
- Ketamine can reverse this by increasing mTOR
- Exercise, enrichment, and coping strategies can help maintain synaptic homeostasis
- After a ketamine infusion, there can be another loss of spines that coincides with the relapse of depression after a single infusion.
- Repeat ketamine therapies and other interventions may maintain the spine number and function.
- For an appointment at NOVA Health Recovery for Ketamine therapy or other medical issues, call us at 703-844-0184 or email us below with your phone number
NOVA Health Recovery is a Ketamine Treatment Center in Fairfax, Virginia (Northern Virginia Ketamine) that specializes in the treatment of depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, OCD, and chronic pain such as CRPS, cluster headaches, and fibromyalgia using Ketamine therapies, both infusion and home-based ketamine nasal spray and oral tablets. We also offer addiction treatment services with Suboxone, Vivitrol, and Sublocade therapies for opiate addiction as well as alcohol treatment regimens.Contact us at 703-844-0184 or at this link: NOVA Health Recovery Ketamine Infusion Center
Ketamine Provider | Ketamine near me | Psychedelic assisted therapy | Mushrooms | Ketamine assisted psychotherapy | Ketamine psychedelic therapy | KAP | K hole | New depression Treatments | Areas we serve:
Maryland (MD):
Bethesda 20814 – Bethesda 20816 – Bethesda 20817 – Chevy Chase 20815 – Colesville 20904 – Cabin John 20815 – Glen Echo 20812 – Gaithersburg 20855 – Gaithersburg 20877- Gaithersburg 20878 – Gaithersburg 20879 – Garrett Park 20896 – Kensington 20895 – Montgomery Village 20886 – Olney 20830 – Olney 20832 – Potomac 20854 – Potomac 20859 – Rockville 20850 – Rockville 20852 – Rockville 20853 – Silver Spring 20903 – Silver Spring 20905 – Silver Spring 20906 – Silver Spring 20910 – Takoma Park 20912 – Wheaton 20902
Washington DC:
Crestwood 20011- North Capitol Hill 20002 – Cathedral Heights 20016 – American University Park 20016 – Columbia Heights 20010 – Mount Pleasant 20010 – Downtown 20036 – Dupont Circle 20009 – Logan Circle 20005- Adams Morgan 20009 – Chevy Chase 20015 – Georgetown 20007 – Cleveland Park 20008 – Foggy Bottom 20037 – Rock Creek Park – Woodley Park 20008 – Tenleytown 20016
Northern Virginia:
McLean 22101- McLean 22102 – McLean 22106 – Great Falls 22066 – Arlington 22201 – Arlington 22202 – Arlington 22203 – Arlington 22205 – Falls Church 22041 – Vienna 22181 – Alexandria 22314 – 22308 -22306 -22305 -22304 Fairfax – 20191 – Reston – 22009 – Springfield – 22152 22015 Lorton 22199
Fairfax, Va
2303 – 22307 – 22306 – 22309 – 22308 22311 – 22310 – 22312
22315 -22003 – 20120 – 22015 – 22027 20121 – 22031 – 20124
22030 – 22033 – 22032 – 22035 – 22039 22041 – 22043
22042 – 22046 – 22044 – 22060 – 22066 20151 – 22079 – 20153 – 22101
22102 – 20171 – 20170 – 22124 – 22151 22150 – 22153
22152 – 20191 – 20190 – 22181- 20192 22180 – 20194 – 22182
Woodbridge – 22191 – 22192 -22193 -22194 – 22195
Springfield – 22150 – 22151 -22152-22153-22154-22155 -22156 – 22157 -22158 -22159 -22160 – 22161
Front Royal 22630
Warren County 22610 22630 22642 22649
Fredericksburg Va 22401 22402 – 22403 – 22404 -22405 -22406 -22407 -22408 – 22412
Please call Sendi Hair Loss Center now at 703-574-0974 for quality Hair Restoration services in Alexandria, VA.
20105 Aldie Loudoun County 20106 Amissville Culpeper County 20107 Arcola Loudoun County
20108 Manassas Manassas City 20109 Sudley Springs Prince William County
20109 Manassas Prince William County 20110 Manassas Manassas City
20111 Manassas Prince William County 20111 Manassas Park Prince William County
20112 Manassas Prince William County 20113 Manassas Park Manassas Park City
20115 Marshall Fauquier County 20116 Marshall Fauquier County
20117 Middleburg Loudoun County 20118 Middleburg Loudoun County
20119 Catlett Fauquier County – 20120 Sully Station Fairfax County
20120 Centreville Fairfax County – 20121 Centreville Fairfax County
20122 Centreville Fairfax County – 20124 Clifton Fairfax County
20128 Orlean Fauquier County -20129 Paeonian Springs Loudoun County
20130 Paris Clarke County
20131 Philomont Loudoun County 20132 Purcellville Loudoun County
20134 Hillsboro Loudoun County 20134 Purcellville Loudoun County
20135 Bluemont Clarke County 20136 Bristow Prince William County
20137 Broad Run Fauquier County 20138 Calverton Fauquier County
20139 Casanova Fauquier County 20140 Rectortown Fauquier County
20141 Round Hill Loudoun County 20142 Round Hill Loudoun County
20143 Catharpin Prince William County
20144 Delaplane Fauquier County20146 Ashburn Loudoun County
20147 Ashburn Loudoun County 20148 Brambleton Loudoun County
20148 Ashburn Loudoun County 20151 Chantilly Fairfax County
20151 Fairfax Fairfax County 20152 South Riding Loudoun County
20152 Chantilly Loudoun County 20152 Fairfax Loudoun County
20153 Chantilly Fairfax County 20153 Fairfax Fairfax County
20155 Gainesville Prince William County 20156 Gainesville Prince William County
20158 Hamilton Loudoun County 20159 Hamilton Loudoun County
20160 Lincoln Loudoun County 20160 Purcellville Loudoun County
20163 Sterling Loudoun County 20164 Sterling Loudoun County
20165 Potomac Falls Loudoun County 20165 Sterling Loudoun County
20166 Dulles Loudoun County 20166 Sterling Loudoun County
20167 Sterling Loudoun County 20168 Haymarket Prince William County
20169 Haymarket Prince William County 20170 Herndon Fairfax County
20171 Oak Hill Fairfax County 20171 Herndon Fairfax County
20172 Herndon Fairfax County 20175 Leesburg Loudoun County
20176 Lansdowne Loudoun County 20176 Leesburg Loudoun County
20177 Leesburg Loudoun County 20178 Leesburg Loudoun County
20180 Lovettsville Loudoun County 20181 Nokesville Prince William County
20182 Nokesville Prince William County 20184 Upperville Fauquier County
20185 Upperville Fauquier County 20186 Warrenton Fauquier County
20187 New Baltimore Fauquier County 20187 Vint Hill Farms Fauquier County 20187 Warrenton Fauquier County
20188 Vint Hill Farms Fauquier County 20188 Warrenton Fauquier County
20190 Reston Fairfax County 20190 Herndon Fairfax County
20191 Reston Fairfax County 20191 Herndon Fairfax County
20194 Reston Fairfax County 20194 Herndon Fairfax County
20195 Reston Fairfax County 20195 Herndon Fairfax County
20197 Waterford Loudoun County 20198 The Plains Fauquier County
Loudon County:
Loudoun County, VA – Standard ZIP Codes
20105 | 20117 | 20120 | 20129 | 20130 | 20132 | 20135 | 20141 | 20147 | 20148 | 20152 | 20158 | 20164 | 20165 | 20166 | 20175 | 20176 | 20180 | 20184 | 20189 | 20197 | 22066